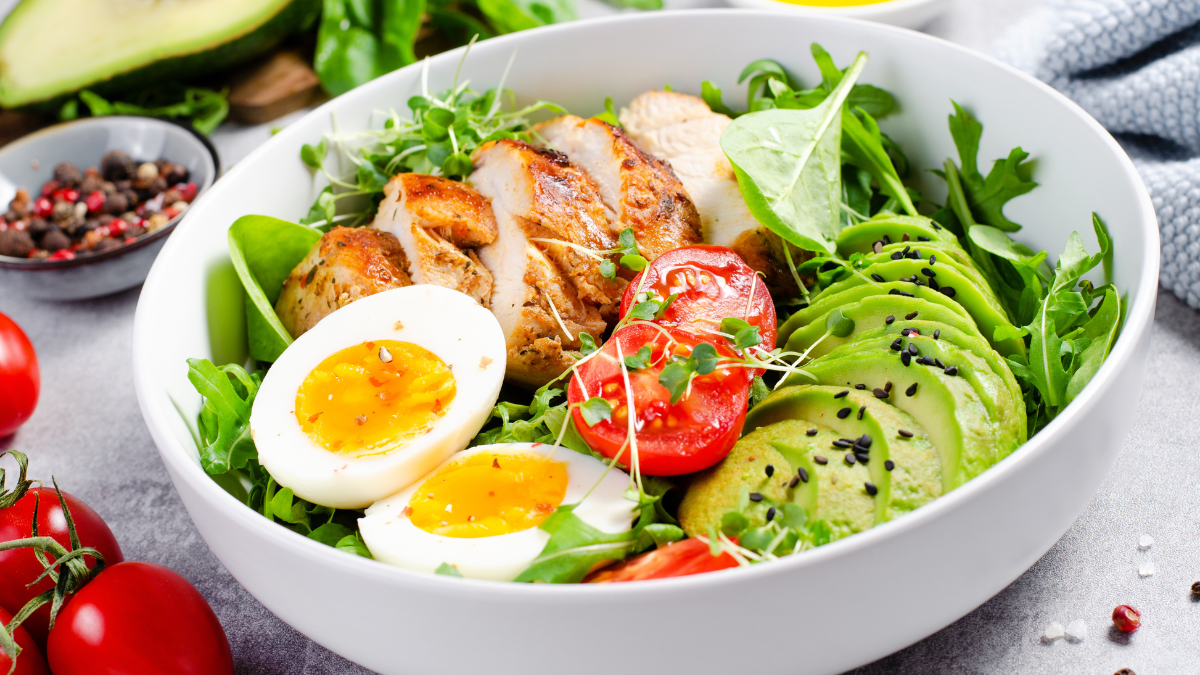
High-Protein Diets: The Ultimate Hack for Fat Loss!
High-protein diets boost metabolism, keep you full longer, and aid weight loss without starvation. Reshape your body with protein! Learn the best ways to maximize its fat-burning benefits today.

Why High-Protein Diets Are a Game-Changer
Losing fat isn’t just about eating less. It’s about eating smarter. High-protein diets help you burn more calories, stay full longer, and preserve muscle while shedding fat. They work because protein has a higher thermic effect than carbs or fats, meaning your body burns more energy digesting it.
Many people struggle with cravings and low energy when cutting calories. Protein helps control hunger hormones, keeping you satisfied for hours. This makes it easier to stick to a diet without constant hunger. It also prevents muscle loss, which is key for long-term fat loss.
A well-balanced diet also supports gut health, which plays a major role in digestion and metabolism. To understand how gut health affects energy and fat loss, check out this guide on the hidden key to energy and vitality.
Unlike fad diets, high-protein diets are sustainable. You don’t need extreme restrictions or complicated meal plans. You simply focus on protein-rich foods while keeping a balanced intake of fats and carbs. Ready to unlock the fat-burning power of protein? Let’s dive in!
What Are High-Protein Diets and How Do They Work?
A high-protein diet focuses on increasing protein intake while balancing fats and carbohydrates. Protein plays a key role in fat loss by boosting metabolism, reducing hunger, and preserving muscle mass. Unlike restrictive diets, this approach allows for sustainable weight loss without extreme food limitations.
How protein helps burn more calories
Protein has a higher thermic effect than other macronutrients. This means the body burns more calories digesting and processing it. When compared to fats and carbohydrates, protein requires more energy to break down. This leads to a natural increase in calorie burn throughout the day.
Increasing protein intake also helps regulate blood sugar. By slowing digestion, protein prevents spikes and crashes in energy levels. Research on how protein-rich meals support metabolism and energy balance shows that higher protein consumption leads to improved fat loss results. Learn more about the connection between protein intake and metabolism by reading this expert breakdown on protein’s role in fat-burning efficiency.
Why protein helps control hunger and cravings
Hunger is a major obstacle in weight loss. Many diets fail because people struggle with constant cravings. Protein naturally suppresses appetite by increasing levels of satiety hormones. It also reduces levels of ghrelin, the hormone responsible for hunger signals.
When meals are high in protein, people feel full longer. This leads to a decrease in overall calorie intake without the need for forced restrictions. Studies show that people who consume more protein throughout the day eat fewer calories without even trying.
How high-protein diets prevent muscle loss
During weight loss, the body often breaks down muscle along with fat. Losing muscle slows metabolism and makes it harder to maintain results. Protein protects lean muscle, ensuring that fat loss comes from stored fat instead of muscle tissue.
Muscle preservation is critical for long-term success. A higher protein intake helps maintain strength, improve body composition, and support overall health. Combining protein with resistance training enhances these effects even further.
High-protein diets are effective because they support fat loss while preserving muscle. They also help regulate hunger and increase calorie burn. Next, let’s explore the science behind why these diets work so well.
The Science Behind High-Protein Diets and Fat Loss
Protein is more than just a building block for muscle. It plays a vital role in metabolism, hormone regulation, and fat loss. High-protein diets have been proven to enhance weight loss by increasing calorie burn, reducing appetite, and preserving lean muscle.
Why protein increases calorie burn naturally
Every food requires energy to digest, but protein demands the most. This process is called the thermic effect of food (TEF). Compared to carbohydrates and fats, protein has a significantly higher TEF, meaning the body burns more calories while digesting it.
Consuming a higher percentage of daily calories from protein leads to an increased metabolic rate. Studies on how dietary protein boosts calorie burning and weight management suggest that people on high-protein plans naturally burn more calories throughout the day. Read more about how protein affects metabolism in this detailed breakdown on dietary protein and fat oxidation.
How protein reduces appetite and regulates hormones
Hunger control is one of the biggest challenges in fat loss. Protein has a direct impact on appetite-regulating hormones. It increases peptide YY and GLP-1, both of which promote fullness, while simultaneously reducing ghrelin, the hormone responsible for hunger.
A meal rich in protein helps people stay full longer. This leads to a natural reduction in calorie intake without the need for extreme restrictions. When protein intake is consistently high, cravings decrease, making it easier to stick to a fat-loss plan.
Why preserving muscle is key to long-term weight loss
Losing weight is not just about shedding fat. If muscle mass decreases, metabolism slows, making it harder to maintain results. Protein prevents this by protecting lean muscle during calorie deficits.
Resistance training combined with a high-protein diet further enhances muscle retention. This keeps metabolism high, ensuring that fat loss continues without loss of strength or energy.
How high-protein diets improve body composition
Weight loss does not always mean fat loss. Many diets cause muscle depletion, leading to a weaker, less toned physique. Increasing protein intake ensures that weight lost comes primarily from fat while maintaining muscle definition.
High-protein diets support fat loss while keeping metabolism strong. They also regulate hunger and help maintain muscle for long-term success. Next, let’s explore the best protein-rich foods for maximizing fat loss.

Best High-Protein Foods for Maximum Fat Loss
The right food choices make all the difference in a high-protein diet. Some proteins build muscle and support fat loss better than others. Eating nutrient-dense, whole foods maximizes results and keeps the body fueled.
Why lean proteins are best for fat loss
Protein comes in many forms. Some are rich in healthy fats, while others are lean and low in calories. Lean protein sources provide the highest amount of nutrients without excess fats. This helps keep total calorie intake in check while preserving muscle.
High-quality proteins also support digestion and metabolism. A breakdown of how protein sources affect fat burning and muscle retention shows that lean proteins are most effective in boosting metabolism while keeping hunger under control. Read more about the impact of different protein types on body composition in this comprehensive guide on optimal protein choices for weight management.
Best animal-based proteins for fat loss
Animal proteins contain all essential amino acids. They help build muscle, improve recovery, and promote fat loss. Choosing lean cuts reduces unnecessary calories while maintaining high protein intake.
- Chicken breast – Low in fat and packed with protein.
- Turkey – High in protein with fewer calories than beef.
- Egg whites – Pure protein with no added fat.
- White fish – Low-calorie options like cod and tilapia.
- Greek yogurt – High in protein with gut-friendly probiotics.
Best plant-based proteins for fat loss
Plant proteins offer fiber, vitamins, and minerals. They support digestion, balance blood sugar, and help with satiety. Mixing different sources ensures all essential amino acids are included.
- Lentils – High in protein and rich in fiber.
- Chickpeas – Help regulate appetite and provide slow-digesting carbs.
- Tofu – A complete protein that absorbs flavors well.
- Quinoa – One of the few plant-based complete proteins.
- Hemp seeds – Provide protein, omega-3s, and healthy fats.
How protein supplements can support a high-protein diet
Whole foods should be the foundation of any diet. However, protein supplements help fill gaps when needed. They provide quick and convenient protein without extra calories.
- Whey protein – Absorbs quickly and supports muscle recovery.
- Casein protein – Slower digestion keeps muscles fueled overnight.
- Plant-based protein powders – Great for those avoiding dairy.
High-protein diets are most effective when built around whole, nutrient-dense foods. Next, let’s explore how to structure a meal plan that maximizes fat loss and muscle retention.
How to Structure a High-Protein Meal Plan
A high-protein diet works best with a structured meal plan. Eating the right balance of protein, fats, and carbs ensures steady energy, fat loss, and muscle retention. Planning ahead also makes it easier to stay consistent.
How to determine daily protein intake
Protein needs vary based on body weight, activity level, and goals. A general guideline is to consume between 0.6 to 1.0 grams of protein per pound of body weight. Athletes and active individuals may require more.
Tracking protein intake helps prevent under-eating or over-consuming calories. A well-planned diet supports muscle recovery and keeps metabolism high. Studies on how protein intake affects muscle preservation and fat loss show that spreading protein intake evenly across meals leads to better results. Read more about optimizing protein distribution in this expert guide on protein timing for muscle retention.
Best meal timing for a high-protein diet
Eating protein-rich meals throughout the day helps control hunger and maintain muscle mass. Spacing meals every 3 to 4 hours prevents energy crashes and keeps metabolism steady.
A simple meal structure includes:
- Breakfast – A protein-packed meal to jumpstart metabolism.
- Lunch – A balanced meal with lean protein and fiber.
- Dinner – A light meal focused on protein and healthy fats.
- Snacks – Small protein-based options to curb cravings.
Sample high-protein meal plan for fat loss
A well-rounded meal plan combines lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbs.
- Breakfast: Scrambled egg whites with spinach and avocado.
- Snack: Greek yogurt with almonds and berries.
- Lunch: Grilled chicken salad with olive oil dressing.
- Snack: Cottage cheese with chia seeds.
- Dinner: Baked salmon with roasted vegetables.
This structure keeps hunger in check and supports muscle growth while losing fat.
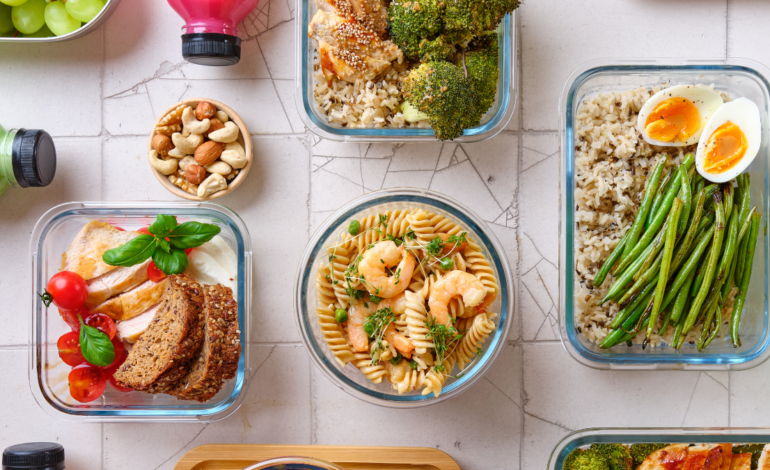
How to meal prep for a high-protein diet
Meal prepping saves time and ensures meals stay balanced. Cooking in batches makes it easier to follow a structured plan. Preparing protein sources in advance prevents last-minute unhealthy choices.
Simple meal prep strategies include:
- Cooking chicken, turkey, or tofu in bulk.
- Pre-portioning meals into containers for convenience.
- Keeping protein-rich snacks readily available.
A high-protein diet becomes effortless with a solid plan. Next, let’s address common myths that often prevent people from getting the best results.
Common Myths About High-Protein Diets Debunked
Misinformation about high-protein diets often prevents people from seeing real results. Many believe protein damages organs, leads to weight gain, or is unnecessary for fat loss. These myths create confusion and discourage healthy eating habits. It’s time to separate fact from fiction.
Does eating too much protein harm the kidneys?
One of the most common concerns is kidney damage. Many believe high protein intake strains the kidneys, leading to long-term health issues. However, research on how protein consumption affects kidney function in healthy adults confirms that high-protein diets do not harm kidney health. Read more about the impact of protein on kidney function in this evidence-based guide on protein intake and kidney health.
For those with pre-existing kidney disease, excessive protein may require monitoring. However, for healthy individuals, a high-protein diet poses no risk when balanced with adequate hydration and whole foods.
Do high-protein diets cause weight gain?
Some assume that eating more protein leads to excess calorie intake and weight gain. While it’s true that consuming too many calories can lead to fat storage, protein itself does not cause weight gain. In fact, it boosts metabolism and promotes fat loss.
Protein has a high thermic effect, meaning the body burns more calories digesting it compared to fats and carbohydrates. It also helps control appetite, reducing the likelihood of overeating. When paired with regular exercise, a high-protein diet supports muscle growth while keeping body fat low.
Is protein only necessary for people who lift weights?
Protein is essential for everyone, not just athletes. It supports muscle repair, regulates hormones, and strengthens the immune system. Even those who do not engage in heavy strength training benefit from higher protein intake.
Older adults need more protein to prevent muscle loss. Those recovering from injuries require protein for tissue repair. Even individuals focused on general wellness see improvements in energy and metabolism by increasing protein consumption.
Can a high-protein diet lead to nutritional deficiencies?
A well-balanced high-protein diet includes a variety of foods. Lean meats, dairy, eggs, legumes, nuts, and seeds provide essential vitamins and minerals. The key is to focus on whole, nutrient-dense sources rather than processed options.
Eating a diverse range of proteins ensures a proper intake of fiber, healthy fats, and micronutrients. Planning meals thoughtfully prevents nutrient gaps and supports overall health.
Misconceptions about high-protein diets often hold people back. Next, let’s compare how they measure up against other popular diets.

High-Protein Diets vs. Other Popular Diets
Choosing the right diet can be overwhelming. Many promise fat loss, better health, and increased energy. High-protein diets stand out because they fuel the body while preserving muscle. But how do they compare to other popular diets?
How high-protein diets differ from low-carb diets
Low-carb diets like Keto and Atkins focus on reducing carbohydrates to force the body into fat-burning mode. While effective, these diets can lead to fatigue and muscle loss if protein intake is too low.
A high-protein diet with moderate carbs supports fat loss while maintaining muscle mass. Unlike strict low-carb plans, it allows for flexibility, making it easier to sustain long-term. Read more about how protein intake impacts metabolic health by exploring this expert breakdown on protein and energy balance.
Is a high-protein diet better than intermittent fasting?
Intermittent fasting limits eating to specific time windows. It helps some people control calorie intake, but it doesn’t prioritize macronutrient balance. Without enough protein, muscle loss becomes a risk.
A structured high-protein diet provides steady energy throughout the day. It also prevents muscle breakdown, which can happen when fasting periods are too long. Those who combine intermittent fasting with a protein-rich diet often see better results.
How plant-based diets compare to high-protein diets
Plant-based eating focuses on whole foods, fiber, and micronutrients. While rich in vitamins, some plant-based diets lack sufficient protein, making muscle maintenance harder.
A high-protein diet can be fully plant-based with the right food choices. Legumes, quinoa, tofu, and nuts provide ample protein without animal products. Mixing these foods ensures a complete amino acid profile for muscle growth and recovery.
Why high-protein diets lead to sustainable fat loss
Many diets focus on short-term results. They cut calories drastically or eliminate entire food groups. This often leads to frustration and weight regain.
A high-protein diet works differently. It boosts metabolism, keeps hunger under control, and preserves lean muscle. This combination helps people lose fat without feeling deprived. It also makes long-term success more achievable.
Diet trends come and go, but protein remains essential. Next, let’s explore the potential risks and side effects of a high-protein approach.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of High-Protein Diets
A high-protein diet offers many benefits, but it’s important to follow it correctly. Too much protein without balance can lead to health concerns. Understanding these risks helps maintain long-term success.
Can eating too much protein cause digestive issues?
Digestive discomfort can happen when protein intake is too high, especially if fiber is too low. Protein-rich foods take longer to break down. This can lead to bloating or constipation if the diet lacks fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Increasing fiber and drinking enough water help digestion. A balanced diet with lean proteins and fiber-rich foods supports gut health. Research on how dietary fiber improves digestion and prevents bloating shows that combining fiber with protein promotes better gut function. Learn more about balancing protein intake with digestion-friendly foods in this guide on optimizing gut health through nutrition.
Does a high-protein diet lead to dehydration?
Protein metabolism requires water. The body eliminates nitrogen waste through urine, which can cause dehydration if water intake is too low. Signs of dehydration include headaches, fatigue, and dry skin.
Drinking enough water is key. A general guideline is to consume extra water with every protein-heavy meal. Electrolytes from whole foods like avocados, bananas, and leafy greens also help maintain hydration.
How protein intake affects kidney function
Healthy kidneys filter excess nitrogen from protein metabolism. Many believe that too much protein strains the kidneys, but this is mostly a myth. High-protein intake does not harm kidney function in healthy individuals.
However, those with pre-existing kidney disease may need to monitor protein intake. A well-balanced diet with moderate protein is the best approach for maintaining kidney health.
Does a high-protein diet increase the risk of nutrient deficiencies?
A protein-focused diet should still include a variety of nutrients. Relying only on meat or protein shakes can lead to vitamin and mineral deficiencies. Essential nutrients like magnesium, potassium, and fiber often come from plant-based sources.
Adding vegetables, fruits, nuts, and seeds ensures a balanced intake. A diverse diet supports muscle growth, energy levels, and overall health.
High-protein diets work best when properly structured. Next, let’s explore how to make them a sustainable lifestyle rather than a short-term fix.
How to Make High-Protein Diets a Lifestyle, Not a Fad
A high-protein diet is more than a short-term fix. It can be a long-term strategy for fat loss, muscle building, and overall health. The key is making it sustainable and enjoyable.
Why flexibility is important in a high-protein diet
Strict dieting leads to burnout. People often abandon restrictive eating plans because they feel deprived. A high-protein approach with balanced meals allows for flexibility while keeping results on track.
Incorporating a variety of protein sources makes meals enjoyable. Alternating between lean meats, fish, dairy, and plant-based options prevents boredom. Research on how diverse protein sources improve diet sustainability suggests that variety leads to better long-term adherence. Learn more about creating a well-rounded meal plan in this expert guide on dietary protein diversity and long-term health.
How to meal prep for long-term success
Planning ahead removes stress. Meal prepping ensures that high-protein meals are always available, reducing the temptation to eat processed foods.
Batch cooking proteins like chicken, turkey, tofu, and beans saves time. Keeping grab-and-go options like Greek yogurt, boiled eggs, and protein bars helps meet daily intake goals.
A sustainable approach includes easy, enjoyable meals. Cooking in bulk, seasoning meals well, and mixing up flavors keep a high-protein diet from becoming repetitive.
How to stay consistent without feeling restricted
Consistency matters more than perfection. Skipping a meal or having a low-protein day won’t ruin progress. The goal is to create habits that fit into everyday life.
Simple changes, like adding protein to breakfast, choosing high-protein snacks, and prioritizing lean meats at dinner, make a big difference. Eating intuitively while keeping protein intake high ensures lasting results.
Why lifestyle changes lead to long-term results
Fad diets promise quick fixes but rarely work long-term. Sustainable eating patterns focus on high-protein meals combined with overall nutrition balance. Eating well, staying active, and making protein a priority create a foundation for lasting health.
A high-protein diet is not a trend. It’s a proven way to improve energy, build muscle, and lose fat. Next, let’s summarize why protein is the ultimate key to long-term fat loss and health.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Fat Loss with Protein
Fat loss is not just about eating less. It’s about eating smarter. A high-protein diet helps burn fat, boost metabolism, and build lean muscle. Unlike fad diets, it provides lasting results without extreme restrictions.
Protein keeps hunger in check. It helps control cravings and supports muscle retention. This makes it easier to lose fat without feeling deprived. Whether your goal is weight loss or muscle gain, increasing protein intake makes a difference.
Sustainability is key. A high-protein diet should be flexible, balanced, and enjoyable. Choosing diverse protein sources, planning meals, and staying consistent lead to long-term success.
Results don’t happen overnight. Small, daily changes build long-lasting habits. Make protein a priority, stay active, and enjoy the process. Your body will thank you.